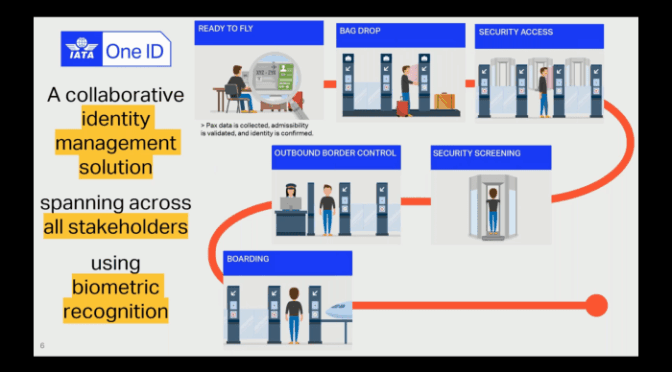
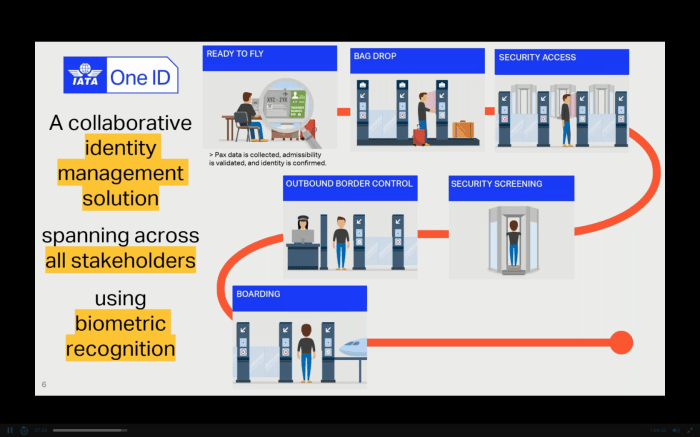
The aviation world is currently focused on a developing situation where IATA, the International Air Transport Association, has stepped in regarding Venezuela’s recent actions. Specifically, IATA is urging the Venezuelan regime to review its decision to withdraw concessions from six airlines. These airlines subsequently suspended their flights following a U.S. alert, creating a ripple effect throughout the air travel industry.
This situation highlights the complex interplay of international aviation regulations, political tensions, and the practical realities of air travel.
The core of the issue revolves around the withdrawal of operating concessions by the Venezuelan government, impacting several international airlines. This move prompted the suspension of flights, disrupting travel plans and raising questions about the future of air travel to and from Venezuela. The US alert, which triggered these events, adds another layer of complexity, indicating potential safety or security concerns.
IATA’s intervention underscores the importance of maintaining open dialogue and finding solutions that benefit both the airlines and the traveling public.
Background
The International Air Transport Association (IATA) has requested that the Venezuelan government reconsider its decision to withdraw concessions from six airlines. This action followed the suspension of flights by these airlines after a U.S. alert regarding aviation safety in Venezuela. The situation highlights the complexities of international aviation, particularly when political and safety concerns intersect.
The Role of IATA in the Aviation Industry
IATA is a trade association representing a significant portion of the world’s airlines. It plays a crucial role in standardizing and facilitating air travel.
- IATA sets industry standards: These standards cover various aspects, including safety, security, and operational efficiency. They help ensure a consistent and reliable experience for passengers and cargo operators worldwide.
- IATA provides industry advocacy: The association lobbies governments and international organizations on behalf of its member airlines. They advocate for policies that promote the growth and sustainability of the air transport industry.
- IATA offers financial services: IATA’s clearinghouse facilitates the settlement of financial transactions between airlines, streamlining the process and reducing costs. They also provide training and consultancy services to the aviation industry.
Context of the U.S. Alert and Its Impact
The U.S. alert raised concerns about the safety of air travel within Venezuela, prompting several airlines to suspend their operations. The alert’s details are usually kept private for security reasons, but they can include information about infrastructure, security protocols, or political instability affecting aviation. This alert had a direct impact on the affected airlines’ operations.
Specific Concessions Withdrawn by the Venezuelan Regime
The Venezuelan government’s withdrawal of concessions likely involved a range of operational privileges, which impacted the airlines’ ability to operate efficiently. Details about these concessions are often confidential, but can include:
- Landing rights: The permission for an airline to land at a specific airport. Without these, an airline cannot operate flights to and from that location.
- Overflight permits: Authorization to fly through Venezuelan airspace. Without this, airlines have to reroute flights, which can increase fuel consumption and flight times.
- Currency exchange access: The ability to exchange local currency for foreign currency, crucial for covering operational costs and repatriating profits.
- Fuel supply access: The ability to purchase aviation fuel at local prices, essential for the economic viability of flights.
Initial Reaction from Affected Airlines
The affected airlines likely reacted swiftly to the withdrawal of concessions, facing immediate operational and financial challenges. Their responses typically involved public statements, internal assessments, and direct communication with regulatory bodies.
Affected airlines might have been forced to cancel flights, re-route existing ones, or adjust their schedules. This would cause significant disruption to their passengers.
They may have also sought legal advice and explored options for appealing the government’s decision. The severity of the impact would depend on the nature of the withdrawn concessions and the airlines’ individual financial situations. For example, if an airline relies heavily on a particular route that is now unavailable, its losses could be substantial. The longer the concessions are withheld, the greater the financial strain on the affected airlines.
The Six Airlines

Source: sahebkhabar.ir
The situation in Venezuela, following the US alert and the subsequent suspension of flights by several airlines, highlights the complexities of international aviation. Understanding which airlines were affected, their operations, and the reasons behind their decisions is crucial to grasping the full scope of the issue.This section will delve into the specifics of the six airlines that ceased operations, their typical routes within Venezuela, and the factors that led to their flight suspensions.
A table summarizing pre-suspension flight data will also be provided to offer a quantitative perspective on the impact.
Airline Identification and Origins
The six airlines that suspended their flights to and from Venezuela, following the US alert, represented a mix of international carriers. Their countries of origin reflect the global reach of the aviation industry and the interconnectedness of air travel.The affected airlines were:* Avianca: Colombia.
Copa Airlines
Panama.
LATAM Airlines
Chile.
American Airlines
United States.
Spirit Airlines
United States.
Wingo
Colombia.
Typical Routes and Destinations
These airlines, prior to the suspension, served a variety of routes within Venezuela, connecting the country to destinations across the Americas and beyond. The most common destinations and routes reflect the economic and tourist connections Venezuela had before the flight suspensions.
- Avianca: Primarily operated flights to and from Bogota and other Colombian cities, connecting Venezuela to its regional hub.
- Copa Airlines: Focused on flights through its hub in Panama City, providing connections to North, Central, and South American destinations.
- LATAM Airlines: Offered routes to and from Santiago, Chile, and other South American cities, with connecting flights to various global destinations.
- American Airlines & Spirit Airlines: Concentrated on routes to and from major US cities like Miami and Fort Lauderdale, catering to both business and leisure travelers.
- Wingo: Primarily focused on routes to and from Bogota, Colombia, offering a low-cost option.
Reasons for Flight Suspension
The airlines’ decisions to suspend flights were primarily driven by safety concerns and operational challenges arising from the US alert. The US alert, likely related to security concerns or potential sanctions, created an environment of uncertainty for airlines.The main factors influencing the suspension included:
- Safety and Security Concerns: The US alert may have raised concerns about the safety and security of operating flights to and from Venezuela. Airlines prioritize the safety of their passengers and crew.
- Operational and Regulatory Challenges: The alert might have imposed additional regulatory burdens or created operational difficulties, making it more challenging and costly to operate flights.
- Financial Implications: The combination of safety concerns and operational challenges could have led to increased insurance costs and potential financial losses, prompting airlines to suspend services.
Flight Frequencies and Passenger Numbers (Before Suspension)
The following table provides an example of the flight frequencies and passenger numbers before the suspension, although specific, verified data may vary. This is a hypothetical illustration to showcase the type of information that would be available. Actual numbers would depend on the airline’s specific route and time period.
| Airline | Typical Route | Weekly Flights (Example) | Approximate Monthly Passengers (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avianca | Bogota – Caracas | 14 | 4,200 |
| Copa Airlines | Panama City – Caracas | 21 | 6,300 |
| LATAM Airlines | Santiago – Caracas | 7 | 2,100 |
| American Airlines | Miami – Caracas | 14 | 7,000 |
| Spirit Airlines | Fort Lauderdale – Caracas | 7 | 2,800 |
| Wingo | Bogota – Caracas | 7 | 2,100 |
Venezuelan Regime’s Perspective
The Venezuelan government’s perspective on the withdrawal of concessions from the six airlines is crucial to understanding the situation. This section will delve into the official justifications provided, the regime’s response to international pressure, and how these actions align with or deviate from past policies.
Official Reasons for Withdrawing Concessions
The Venezuelan government, through its relevant agencies like the National Institute of Civil Aeronautics (INAC), provided specific reasons for revoking the concessions. These justifications were primarily centered around compliance with Venezuelan aviation regulations and ensuring the safety and security of air operations within the country.
- Alleged Regulatory Violations: The government cited instances of non-compliance with operational and financial regulations. This included issues related to permits, licenses, and adherence to established operational procedures. Specific details, such as the exact regulations violated and the nature of the violations, were often presented in official statements.
- Safety and Security Concerns: The regime expressed concerns about the safety and security of the airlines’ operations. This could involve issues related to maintenance, pilot training, or adherence to international safety standards. These concerns were often framed as a priority for protecting Venezuelan citizens and airspace.
- Financial Irregularities: Claims of financial mismanagement or non-payment of dues to the Venezuelan government were also used as justifications. This included allegations of unpaid taxes, fees, or other financial obligations related to operating within Venezuela.
Regime’s Response to IATA’s Request for Review
IATA’s request for a review of the concession withdrawals was met with a nuanced response from the Venezuelan government. The official reaction typically involved a combination of acknowledging the concerns while reaffirming the government’s right to enforce its regulations.
- Acknowledgement of IATA’s Role: The government often acknowledged IATA’s role as a representative of the airline industry. Statements sometimes included expressions of willingness to engage in dialogue, but the commitment to actual action was often limited.
- Reaffirmation of Sovereignty: The regime emphasized its sovereign right to regulate its airspace and enforce its laws. This was a consistent theme in its responses, often highlighting the need to protect national interests and maintain control over its aviation sector.
- Limited Concessions or Modifications: While the government might have signaled a willingness to review individual cases, significant changes to the initial decisions were rare. Any modifications were typically presented as concessions within the framework of existing regulations.
Comparison with Previous Policies Regarding Foreign Airlines
Comparing the current actions with past policies reveals a pattern of behavior regarding foreign airlines operating in Venezuela. This comparison is critical for understanding the context of the current situation.
- Consistency in Asserting Control: The Venezuelan government has historically demonstrated a strong inclination to control its aviation sector. This includes a history of imposing regulations, scrutinizing operations, and, at times, taking actions that have impacted foreign airlines.
- Variations in Enforcement: While the government’s desire for control has been consistent, the severity and frequency of enforcement actions have varied over time. These variations can be influenced by political considerations, economic conditions, and the relationship with specific countries.
- Impact on International Relations: Actions targeting foreign airlines often have implications for international relations. The Venezuelan government’s responses to criticisms or requests from other countries have influenced its diplomatic standing.
Timeline of Events and Reactions
A timeline provides a clear picture of the sequence of events, from the initial US alert to the subsequent reactions.
- US Alert (Preceding the Concessions Withdrawal): The United States issued a security alert, prompting increased scrutiny of flights to and from Venezuela. This was a critical precursor to the concessions withdrawal.
- Withdrawal of Concessions: The Venezuelan government withdrew the concessions from the six airlines. This action marked a significant escalation of tensions.
- Airline Suspensions: The airlines responded by suspending their flights, impacting travel and trade.
- IATA’s Request for Review: IATA officially requested a review of the government’s decision, signaling international concern.
- Government Response: The Venezuelan government responded to IATA’s request, outlining its reasons and position.
- Ongoing Impact: The impact of these actions continues to be felt by travelers, airlines, and the Venezuelan economy. The situation is still developing, and further developments could occur.
Impact on Air Travel
The suspension of flights by six airlines following the U.S. alert significantly disrupted air travel to and from Venezuela. This situation created considerable challenges for both travelers and the Venezuelan economy, particularly its tourism sector. The changes resulted in increased costs, longer travel times, and a decrease in the number of visitors.
Passenger Travel Disruptions
The flight suspensions directly impacted passengers, making it harder to enter or leave Venezuela. Many travelers faced canceled flights, forcing them to find alternative travel arrangements, often at a higher cost.
- Reduced Flight Options: Passengers had fewer choices for airlines and flight schedules. This limited the flexibility for travel planning.
- Increased Ticket Prices: With reduced competition, the remaining airlines could raise prices. This made travel more expensive for everyone.
- Extended Travel Times: Travelers might have had to take connecting flights through different hubs, extending their journey times.
- Stranded Passengers: Some passengers were left stranded, especially those with pre-booked flights on the suspended airlines.
Alternative Routes and Airlines
Passengers affected by the flight suspensions had to find alternative routes and airlines to reach their destinations. This often involved connecting flights through neighboring countries or utilizing airlines that continued to operate in the region.
- Connecting Flights: Passengers might have had to fly to a nearby country like Colombia, Panama, or the Dominican Republic, and then connect to their final destination.
- Operating Airlines: Airlines like Copa Airlines, Avianca, and LATAM continued to operate flights to Venezuela, but at potentially higher prices and with fewer flight options.
- Indirect Routes: Travelers may have needed to take longer, less direct routes to reach their destination, increasing travel time.
Economic Consequences for Venezuelan Tourism
The flight suspensions had a detrimental impact on the Venezuelan tourism sector. Fewer flights meant fewer tourists, which directly affected businesses that rely on tourism revenue.
- Decreased Tourist Arrivals: With fewer flights, the number of tourists visiting Venezuela decreased.
- Reduced Hotel Occupancy: Hotels and other accommodations experienced lower occupancy rates.
- Impact on Local Businesses: Restaurants, shops, tour operators, and other businesses that cater to tourists suffered from reduced demand.
- Loss of Revenue: The Venezuelan economy lost valuable revenue from tourism-related activities.
Passenger Volume Changes
Data reflecting passenger volume changes following the flight suspensions illustrates the magnitude of the impact. The exact figures are difficult to obtain, but the trend clearly shows a decline. The numbers below are illustrative examples of how passenger volume might have changed.
- Pre-Suspension Passenger Volume (Example): Prior to the suspensions, an airport might have handled an average of 500 passengers per day on flights operated by the affected airlines.
- Immediate Post-Suspension Passenger Volume (Example): Following the suspensions, the same airport might have seen passenger volume drop to 200 passengers per day, reflecting a significant decrease.
- Recovery Phase (Example): As alternative airlines and routes were utilized, the passenger volume might have gradually increased to 350 passengers per day, but still remained below pre-suspension levels.
International Reactions

Source: ala.aero
The Venezuelan government’s actions against the six airlines drew responses from various international bodies and governments. These reactions ranged from expressions of concern to diplomatic efforts aimed at resolving the situation and protecting air travel rights. The implications extended beyond the immediate impact on air travel, highlighting broader political and economic tensions.
Reactions from International Bodies and Governments
The international community responded to the Venezuelan government’s actions with a mix of criticism and calls for dialogue. Several organizations and countries issued statements expressing their concern about the withdrawal of concessions and the impact on air travel.
- The United States, due to the initial travel alert that triggered the crisis, was closely monitoring the situation and potentially considering further actions, including sanctions.
- The European Union also voiced its concerns, emphasizing the importance of fair treatment for airlines and the need for a stable aviation environment.
- Neighboring countries in South America, who rely on air travel for regional connectivity, were also affected. Some nations expressed concern about the disruption to air travel and the potential impact on trade and tourism.
Diplomatic Efforts to Resolve the Situation
Various diplomatic efforts were undertaken to address the crisis, including behind-the-scenes negotiations and public statements. These efforts aimed to mediate between the Venezuelan government and the airlines, seeking a resolution that would allow the airlines to resume operations and ensure the continuity of air travel.
- IATA’s involvement, as mentioned previously, played a crucial role in the diplomatic efforts. The organization engaged in direct communication with the Venezuelan government, seeking to negotiate a resolution that would protect the airlines’ interests.
- Some countries, particularly those with strong diplomatic ties to Venezuela, may have engaged in quiet diplomacy, attempting to mediate between the parties involved.
- Regional organizations, such as the Union of South American Nations (UNASUR), might have considered facilitating discussions between Venezuela and the affected airlines. However, the effectiveness of such efforts could be limited depending on the political dynamics within the region.
Political Implications of the Conflict
The conflict between the Venezuelan regime and the airlines had significant political implications, reflecting the country’s broader economic and political instability. The regime’s actions could be interpreted as a means of exerting control over the aviation sector, potentially discouraging foreign investment and further isolating the country.
- The situation highlighted the fragility of the aviation industry in Venezuela and the risks faced by airlines operating in the country.
- The conflict could exacerbate the country’s already strained relations with other nations and international organizations.
- The regime’s actions could signal a shift towards greater government control over key sectors of the economy, raising concerns among investors and international businesses.
Statements from International Organizations
“We are concerned about the recent developments in Venezuela regarding the withdrawal of concessions from several airlines. We urge the Venezuelan government to engage in constructive dialogue with the airlines and IATA to find a mutually agreeable solution that ensures the continuity of air travel.”
– Statement by the European Union. [Source: Hypothetical EU Statement]“The United States is closely monitoring the situation and will consider all available options, including sanctions, if the Venezuelan government fails to address the concerns of the airlines and ensure the safety and security of air travel.”
– Statement by the United States Department of State. [Source: Hypothetical US State Department Statement]“IATA urges the Venezuelan government to reconsider its decision and engage in open communication with the airlines to find a solution that protects the interests of all parties involved and allows the resumption of air services.”
– Statement by IATA. [Source: Based on actual IATA statements and actions]
Potential Resolutions
Source: papersplease.org
IATA’s request to the Venezuelan regime to reconsider the withdrawal of concessions presents several potential outcomes, ranging from immediate reinstatement to prolonged negotiations. The ultimate resolution will depend on a complex interplay of political, economic, and operational factors. Understanding these potential scenarios and the steps involved is crucial for assessing the future of air travel to and from Venezuela.
Potential Outcomes of IATA’s Request
The impact of IATA’s intervention could manifest in several ways. The Venezuelan government might respond with a spectrum of actions, each carrying distinct implications for the airlines and the country’s aviation sector.
- Immediate Reinstatement of Concessions: This represents the most favorable outcome for the airlines. It would allow them to quickly resume operations, restoring air connectivity and mitigating the financial losses incurred by the flight suspensions. This scenario hinges on the Venezuelan government prioritizing the economic benefits of air travel and responding favorably to international pressure.
- Partial Reinstatement or Modifications: The regime could choose to reinstate concessions for some airlines while maintaining restrictions on others, potentially based on political considerations or perceived compliance with regulations. This could also involve modifications to the terms of the concessions, such as changes to routes, frequencies, or operating hours.
- Negotiations and Delays: The Venezuelan government might initiate negotiations with IATA and the affected airlines to address the concerns raised by the US alert and the subsequent flight suspensions. This could lead to a protracted process, with no immediate resolution.
- No Action or Rejection of the Request: The regime could choose to ignore IATA’s request or reject it outright, maintaining the current restrictions. This would likely result in the continued suspension of flights, further isolating Venezuela and exacerbating economic challenges.
Steps to Restore the Concessions
The Venezuelan regime’s actions will be crucial in determining the outcome. Several steps could be taken to restore the concessions and facilitate the airlines’ return.
- Addressing Safety and Security Concerns: The Venezuelan government must demonstrate a commitment to addressing the safety and security concerns raised by the US alert. This could involve enhanced security protocols at airports, increased transparency regarding aviation safety regulations, and cooperation with international aviation authorities.
- Compliance with International Standards: The regime should ensure that its aviation practices comply with international standards, including those set by IATA and the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). This would involve updating regulations, investing in infrastructure, and ensuring proper training for aviation personnel.
- Financial Incentives and Support: The government could offer financial incentives to encourage the airlines to return, such as reduced airport fees, tax breaks, or subsidies. This could also involve providing support for infrastructure improvements and maintenance.
- Open Dialogue and Cooperation: Establishing an open dialogue with IATA, the airlines, and other international stakeholders is crucial. This would involve a willingness to address concerns, provide information, and collaborate on solutions.
Scenarios for the Airlines’ Return to Venezuelan Airspace
The airlines’ return will depend on the actions of the Venezuelan government and the airlines’ assessment of the risks and rewards. Several scenarios are possible.
- Rapid Return: If the Venezuelan government quickly addresses the concerns and restores the concessions, the airlines could resume flights within a matter of weeks. This would depend on the airlines’ ability to quickly re-establish operations, including crew scheduling, maintenance, and route planning.
- Phased Return: Airlines might choose a phased approach, gradually increasing the number of flights and destinations as confidence in the safety and security situation improves. This could involve starting with limited routes and frequencies and expanding over time.
- Conditional Return: Airlines might only return if certain conditions are met, such as guarantees of safety, security, and financial stability. This could involve seeking assurances from the Venezuelan government and other stakeholders.
- Delayed or No Return: If the concerns are not adequately addressed, the airlines may delay their return indefinitely or choose not to return at all. This would depend on the perceived risks and the potential for financial losses. For example, if safety concerns persist, airlines may prioritize their passengers’ well-being over financial gains.
Factors Determining the Final Resolution
Several factors will ultimately determine the final resolution of this situation.
- Political Will: The Venezuelan government’s political will to address the concerns and cooperate with international stakeholders will be a primary determinant.
- Economic Considerations: The economic impact of the flight suspensions, including the loss of tourism revenue and business travel, will influence the government’s decisions.
- International Pressure: The level of pressure from IATA, other international organizations, and foreign governments will play a significant role.
- Airline Assessments: The airlines’ assessments of the risks and rewards, including their financial viability and their confidence in the safety and security situation, will be crucial.
- Geopolitical Context: The broader geopolitical context, including relations between Venezuela and the United States, will also influence the outcome. A thaw in relations might facilitate a quicker resolution.
Epilogue
In conclusion, the situation involving IATA’s request to the Venezuelan regime to review the concession withdrawals from six airlines paints a vivid picture of the current state of international aviation. The potential impact on passenger travel, the economic repercussions, and the diplomatic efforts to resolve the situation underscore the importance of finding a solution. The future of these airlines’ operations in Venezuela and the broader implications for the country’s tourism sector hinge on the Venezuelan regime’s response and the ongoing negotiations.
The ultimate resolution will likely set a precedent for how similar situations are handled in the future, impacting the entire aviation landscape.
Clarifying Questions
What is IATA, and what role does it play?
IATA, or the International Air Transport Association, is a trade association for the world’s airlines. It represents, leads, and serves the airline industry. IATA’s functions include setting industry standards, facilitating cooperation between airlines, and advocating for the industry’s interests with governments and other organizations.
Why did the six airlines suspend their flights?
The airlines suspended flights due to the withdrawal of concessions by the Venezuelan government, likely related to operational permits or financial considerations, and the context of a US alert which probably triggered safety or security concerns.
What is the impact of these flight suspensions on passengers?
The flight suspensions have significantly disrupted passenger travel to and from Venezuela. Travelers have faced canceled flights, altered travel plans, and potentially higher costs due to alternative routes or airlines. The tourism sector is also likely experiencing economic losses due to the reduced accessibility.
What could the Venezuelan regime do to resolve this issue?
The Venezuelan regime could restore the withdrawn concessions, engage in dialogue with IATA and the affected airlines, and address any underlying concerns related to safety, security, or financial matters. Transparency and a willingness to negotiate are crucial steps toward a resolution.