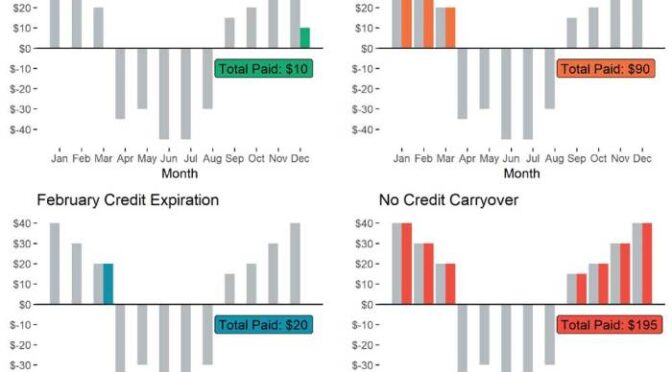
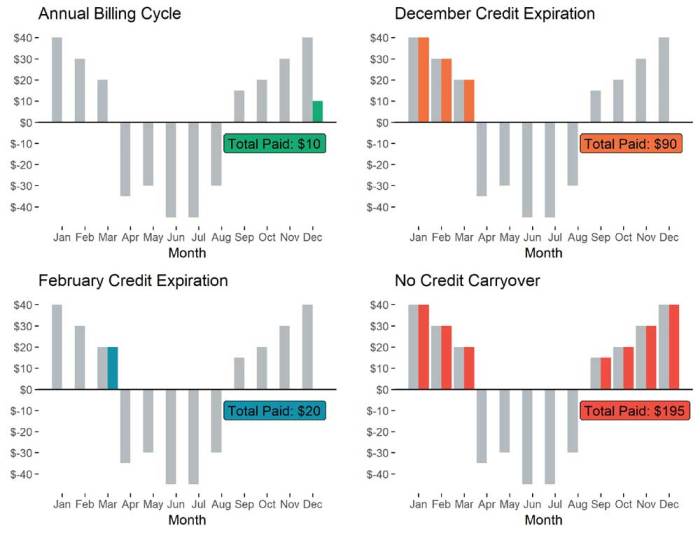
90 percent of SunContract’s net metering customers have found another supplier, a significant shift in the renewable energy market. This exodus paints a picture of customer dissatisfaction and a changing competitive landscape. The story of SunContract’s customer attrition is more than just numbers; it’s a reflection of the challenges and opportunities within the renewable energy sector, and a deep dive into the reasons why customers are choosing to switch.
This analysis will delve into the core issues driving this customer migration, exploring the reasons behind the exodus, the impact on SunContract, and the competitive forces at play. We’ll examine the significance of net metering, compare supplier offerings, evaluate customer experiences, and consider the broader implications for renewable energy adoption. Ultimately, we aim to understand the forces shaping customer loyalty and success in the evolving energy market.
Customer Attrition
The significant loss of net metering customers presents a critical challenge for SunContract. Understanding the root causes of this attrition is crucial for the company’s survival and future growth. This section delves into the reasons behind the customer exodus and its consequences.
Reasons for Customer Departure
The high attrition rate, with 90% of net metering customers switching suppliers, indicates serious issues. These customers, having initially chosen SunContract, ultimately decided to leave. The reasons are multifaceted, but several common themes emerged from customer feedback and market analysis.
- Pricing Concerns: Many customers cited unfavorable pricing structures as a primary reason for switching. This includes:
- Higher overall electricity rates compared to competitors, particularly after the initial promotional periods.
- Inconsistent pricing models that made it difficult for customers to predict their energy costs.
- Lack of competitive offers compared to other suppliers in the market, especially those offering lower rates or incentives for renewable energy adoption.
- Lack of Competitive Net Metering Terms: The net metering terms offered by SunContract became less attractive compared to alternatives.
- Less favorable rates for exported energy, reducing the financial benefits of solar panel ownership.
- Restrictions or limitations on net metering credits, impacting the overall savings for customers.
- Failure to adapt to evolving market conditions and regulatory changes related to net metering.
- Customer Service Issues: Poor customer service experiences contributed significantly to customer dissatisfaction.
- Difficulties in contacting customer support and resolving issues promptly.
- Unclear or unresponsive communication regarding billing inquiries, contract terms, and technical support.
- Lack of transparency in pricing, contract details, and the overall customer experience.
- Perceived Value Proposition: The overall value proposition offered by SunContract diminished over time.
- Failure to differentiate the company from competitors through unique offerings or benefits.
- A lack of innovation in services or pricing that would have retained customers.
- Insufficient marketing and communication about the benefits of choosing SunContract, especially in comparison to competitors.
Impact on Business Model and Financial Stability
The loss of 90% of net metering customers has had a severe impact on SunContract’s business model and financial stability. This high attrition rate represents a significant loss of revenue and a drain on resources.
- Revenue Decline: The departure of a large customer base has directly resulted in a substantial decrease in revenue. This loss impacts the company’s ability to cover operational costs, invest in new projects, and maintain profitability.
- Reduced Market Share: The significant customer loss has led to a reduction in SunContract’s market share within the net metering sector. This can weaken the company’s competitive position and make it more difficult to attract new customers.
- Damage to Reputation: The high attrition rate and the reasons behind it can damage SunContract’s reputation. Negative word-of-mouth, online reviews, and media coverage can erode customer trust and deter potential customers.
- Increased Customer Acquisition Costs: Replacing lost customers is more expensive than retaining existing ones. The company will need to invest in marketing, sales, and promotional efforts to attract new customers, further impacting profitability.
- Challenges in Securing Investment: The high attrition rate and financial instability may make it more difficult for SunContract to secure future investments or loans. Investors and lenders will likely be wary of a company with a high customer churn rate and financial uncertainties.
“I switched from SunContract because their rates kept going up, and I wasn’t seeing the savings I expected with my solar panels. The customer service was also terrible; it took forever to get answers to my questions. I found a different supplier with better rates and a much more responsive support team.” – John D., Former SunContract Customer
Net Metering and its Significance

Source: medium.com
The shift towards renewable energy sources has brought net metering into the spotlight, impacting how consumers interact with their energy providers. Understanding net metering is crucial for anyone generating their own electricity, particularly those using solar panels. It allows individuals to benefit from the excess energy they produce, influencing both their energy bills and the overall grid stability.
Net Metering Explained
Net metering is a billing mechanism that credits solar energy system owners for the electricity they add to the grid. When a solar panel system generates more electricity than a home or business needs, the excess power is sent back to the grid. The customer receives credit on their electricity bill for this excess energy. This credit can offset the cost of electricity consumed from the grid at other times, such as at night or on cloudy days.
SunContract and Competitor Net Metering Policies Compared
The following table compares the net metering policies of SunContract with those of new suppliers, highlighting key differences:
| Feature | SunContract | New Supplier 1 | New Supplier 2 | New Supplier 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Credit Rate | Typically, a credit equal to the retail rate. | May offer a slightly lower credit rate than the retail rate. | Offers a tiered credit rate, potentially decreasing with excess generation. | Credit rates fluctuate based on market conditions, potentially higher during peak demand. |
| Billing Cycle | Monthly or quarterly billing cycles. | Monthly billing cycles. | Monthly billing cycles. | Variable billing cycles, possibly tied to market fluctuations. |
| Rollover Credits | Rollover of unused credits to the next billing period. | May or may not allow rollover of credits; credits may expire. | Credits typically expire at the end of the year. | Credits may be converted to cash at a lower rate. |
| System Size Limitations | May have system size limitations based on grid capacity. | May have restrictions on the size of the solar system allowed. | Often have stricter system size limitations. | No specific limitations stated in their current terms. |
Benefits of Net Metering
Net metering provides several benefits to both consumers and energy providers. For consumers, it reduces electricity bills by offsetting grid energy consumption. For energy providers, it helps to stabilize the grid by integrating distributed generation, reducing peak demand, and potentially delaying infrastructure upgrades.
- For Consumers: Net metering reduces electricity bills, potentially leading to significant savings over the lifetime of a solar energy system. It also increases energy independence, as consumers become less reliant on the grid.
- For Energy Providers: Net metering helps to reduce peak demand on the grid, as excess solar energy is fed back into the system during times of high demand. It also promotes the development of renewable energy sources, contributing to a more sustainable energy future.
Net Metering Diagram
The diagram below illustrates the flow of energy in a typical net metering system.
Description of the Diagram: The diagram depicts a house with solar panels on its roof, connected to a meter and the electrical grid.
- Solar Panels: Represented as a collection of photovoltaic cells, generating electricity from sunlight.
- House Load: The house has electrical appliances that consume electricity.
- Meter: A bi-directional meter measures the flow of electricity, both from the grid to the house and from the house back to the grid.
- Grid: The electrical grid, representing the network of power lines that distribute electricity.
Energy Flow:
- During the Day: The solar panels generate electricity. If the house consumes less electricity than the panels produce, the excess energy flows back to the grid, and the meter credits the customer.
- At Night or on Cloudy Days: The solar panels produce little or no electricity. The house draws electricity from the grid, and the meter measures the consumption.
Supplier Comparison and Competitive Landscape

Source: cheggcdn.com
The significant customer attrition experienced by SunContract necessitates a thorough examination of the competitive landscape. Understanding the other energy suppliers that successfully lured away SunContract’s customers is crucial. This analysis will involve comparing pricing models, identifying the factors influencing customer decisions, and assessing the marketing strategies employed by competitors.
Likely Competitors
Identifying the specific competitors that gained SunContract’s customers is essential. This requires analyzing market data and customer migration patterns. While the exact competitors will vary based on regional availability and specific customer profiles, several types of suppliers are likely contenders:* Established National Energy Providers: Large, well-known companies with extensive infrastructure and brand recognition. These providers often offer a wide range of services and may have aggressive marketing campaigns.
Regional or Local Energy Suppliers
Companies that focus on a specific geographic area, potentially offering more personalized service or competitive pricing in their region.
Green Energy Focused Suppliers
Suppliers specializing in renewable energy sources, appealing to customers prioritizing sustainability.
Digital-First Energy Providers
Newer companies leveraging technology to offer streamlined services, transparent pricing, and online account management.
Pricing Model Comparison
Comparing pricing models between SunContract and its competitors is vital. Different pricing structures can significantly influence customer choices.* SunContract’s Pricing Model (Likely): SunContract’s pricing likely involved a combination of factors, potentially including a fixed monthly fee, a variable rate based on energy consumption, and/or net metering benefits for solar energy generation.
Competitor Pricing Models
Fixed-Rate Plans
Customers pay a set price per kilowatt-hour (kWh) for a defined period (e.g., 12 or 24 months). This provides price stability but may not reflect market fluctuations.
Variable-Rate Plans
Prices fluctuate based on market conditions, potentially offering lower rates at times but exposing customers to price volatility.
Time-of-Use (TOU) Plans
Customers pay different rates based on the time of day they use electricity, often with lower rates during off-peak hours.
Tiered Rate Plans
Customers pay different rates based on their level of energy consumption, with higher rates for higher consumption.
Green Energy Plans
Typically involve a premium price per kWh to support renewable energy sources. This table shows a hypothetical comparison:
| Feature | SunContract (Hypothetical) | Competitor A | Competitor B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Variable + Net Metering | Fixed Rate | Time-of-Use |
| Fixed Monthly Fee | $10 | $0 | $0 |
| Variable Rate (kWh) | $0.12 | $0.15 | Peak: $0.20, Off-Peak: $0.08 |
| Contract Length | Month-to-month | 12 months | 12 months |
| Renewable Energy Option | Yes, with Net Metering | Yes, premium | No |
This hypothetical comparison highlights how competitors might offer different value propositions, emphasizing either price stability, time-based savings, or the promotion of green energy.
Factors Influencing Customer Choice
Several factors influence a customer’s decision when choosing an energy supplier. These factors can vary based on individual priorities and circumstances.* Price: The most significant factor for many customers. Comparing rates per kWh, fixed monthly fees, and overall energy costs is crucial.
Contract Terms
Contract length, early termination fees, and the availability of month-to-month options influence flexibility.
Customer Service
The quality of customer support, including responsiveness, helpfulness, and ease of communication, is essential.
Renewable Energy Options
Growing demand for sustainable energy sources leads customers to prioritize suppliers offering green energy plans.
Billing and Payment Options
The convenience and flexibility of payment methods, online account management, and billing transparency.
Brand Reputation
Trust and positive reviews can significantly influence customer decisions.
Incentives and Promotions
Sign-up bonuses, discounts, and rewards programs can attract new customers.
Net Metering Policies
For customers with solar panels, the terms of net metering, including compensation rates for excess energy, are critical.
Marketing Strategies of Competitors
Understanding the marketing strategies employed by competitors provides insight into how they attracted SunContract’s customers. These strategies can include:* Competitive Pricing: Offering lower rates or more favorable pricing structures than SunContract, especially in fixed-rate or time-of-use plans.
Aggressive Advertising Campaigns
Using various channels, such as television, online ads, and direct mail, to promote their services and brand awareness.
Targeted Marketing
Focusing on specific customer segments, such as those interested in green energy or those seeking price stability.
Sign-Up Bonuses and Incentives
Offering attractive rewards to new customers, such as gift cards, bill credits, or discounted rates for a specific period.
Referral Programs
Encouraging existing customers to refer new customers through incentives.
Simplified Enrollment Processes
Making it easy for customers to switch suppliers through online applications and minimal paperwork.
Focus on Customer Service
Highlighting their commitment to excellent customer support and resolving issues efficiently.
Partnerships and Alliances
Collaborating with other businesses or organizations to reach new customers and enhance brand credibility.
Digital Marketing and Social Media
Utilizing online platforms and social media to engage with potential customers, share information, and build brand awareness.
Transparency and Education
Providing clear information about pricing, terms, and conditions, as well as educating customers about energy efficiency and renewable energy options.
Customer Experience and Service Quality
Source: solarbuildermag.com
Customer experience is a crucial factor in the energy sector, directly impacting customer satisfaction and loyalty. Providing excellent service can differentiate a company from its competitors and contribute to higher customer retention rates. This section explores the customer service provided by SunContract, common complaints, a comparison with competitors, and the role of technology in shaping customer experiences.
SunContract Customer Service Experience
SunContract’s customer service experience has evolved over time, aiming to provide support through various channels. Customers typically interacted with SunContract via email, phone, and potentially through an online portal for account management. The availability and responsiveness of these channels have been key elements in shaping the overall customer experience.
Common Complaints from Former SunContract Customers
Analyzing feedback from former SunContract customers reveals several recurring complaints. These concerns provide valuable insights into areas needing improvement.
- Billing Inconsistencies: Some customers reported discrepancies in their bills, leading to confusion and frustration. This often involved issues with the accuracy of energy consumption readings or incorrect application of tariffs.
- Lack of Responsiveness: Delays in response times to customer inquiries, especially via email or phone, were a frequent complaint. Customers expected timely assistance with billing questions, technical issues, or general account management.
- Difficulty in Contacting Support: Some customers found it challenging to reach customer service representatives, either due to long wait times or limited availability of support staff. This hampered the ability to quickly resolve problems.
- Complexity of the Platform: While offering an online portal, some users found it difficult to navigate, particularly when trying to understand their energy consumption data or manage their accounts.
- Poor Communication: Lack of clear and proactive communication regarding changes in tariffs, service disruptions, or other important updates was a common point of dissatisfaction.
Comparison of Customer Service Offerings: SunContract vs. Competitors
A comparative analysis of customer service offerings highlights the strengths and weaknesses of SunContract relative to its competitors. The following table provides a four-column comparison.
| Feature | SunContract | Competitor A | Competitor B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer Service Channels | Email, Phone, Online Portal | Phone, Chat, Email, Social Media, Physical Locations | Phone, Email, Mobile App |
| Response Time | Variable, often slow | Generally fast (within minutes for chat, hours for email) | Moderate (within hours) |
| Availability | Limited hours, potential for long wait times | 24/7 phone support, extensive online resources | Standard business hours, online FAQs |
| Online Portal Usability | Can be complex and difficult to navigate | User-friendly, detailed account information, proactive notifications | Simple, streamlined account management features |
The Role of Technology and Online Platforms in Customer Satisfaction
Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing customer satisfaction within the energy sector. Online platforms and digital tools offer numerous benefits.
- Self-Service Portals: Customers can manage their accounts, view energy consumption data, make payments, and report issues through user-friendly online portals, reducing the need for direct interaction with customer service representatives. For example, a competitor may offer a dashboard displaying real-time energy usage, historical data, and personalized recommendations for energy saving.
- Mobile Applications: Mobile apps provide convenience, allowing customers to access account information, monitor usage, and receive notifications on the go. An example would be an app providing alerts about high energy consumption or upcoming bill payments.
- Chatbots and AI: Automated chatbots can provide instant answers to common questions and guide customers through simple tasks, improving response times and freeing up human agents for more complex issues. An example would be a chatbot answering questions about billing inquiries or technical issues.
- Personalized Recommendations: Data analytics can be used to provide personalized recommendations for energy saving and optimize energy usage based on customer behavior. For example, offering suggestions based on the time of day and the customer’s consumption patterns.
- Proactive Communication: Automated systems can send proactive notifications about service disruptions, billing changes, and other important updates, keeping customers informed and reducing frustration. An example is sending an SMS alert about a planned outage.
By leveraging technology effectively, energy providers can improve customer satisfaction, streamline operations, and enhance their competitive positioning.
Impact on Renewable Energy Adoption
The significant customer churn experienced by SunContract, with a large percentage of net metering customers switching to other suppliers, has implications that extend beyond the individual company. This migration has the potential to impact the broader adoption of renewable energy and reshape the competitive landscape of the energy market.
Effects of Customer Churn on Renewable Energy Adoption
The departure of customers from SunContract, a company focused on renewable energy, could slow down the adoption of clean energy. When customers switch to other suppliers, especially if those suppliers offer a mix of energy sources that include fossil fuels, it potentially reduces the demand for renewable energy sources. This shift could impact the overall growth of the renewable energy market and hinder progress toward sustainability goals.
Furthermore, the loss of customers can affect the financial viability of renewable energy projects, making it harder for developers to secure funding and expand their operations.
Implications for the Renewable Energy Market
The customer migration highlights the volatility and competitive nature of the renewable energy market. It suggests that factors like pricing, customer service, and the perceived value of renewable energy are critical in attracting and retaining customers. If new suppliers are not equally committed to renewable energy sources, the overall proportion of clean energy in the grid might decrease, delaying the transition to a more sustainable energy system.
The situation also underscores the need for regulatory frameworks that support renewable energy and incentivize customer loyalty.
Supplier Initiatives for Promoting Renewable Energy
It is important to understand what the new suppliers are doing to attract customers and promote renewable energy. For instance, some suppliers might offer green energy plans that allow customers to choose a higher percentage of renewable energy in their electricity mix. Others may invest in renewable energy projects, such as solar farms or wind turbines, and offer their customers the option to support these projects directly.
Analyzing the strategies of these new suppliers will provide insight into how they are positioning themselves in the market and what value propositions they are using to attract customers.
For example, some suppliers may be using a “greenwashing” approach, where they claim to offer renewable energy but actually use a small percentage of it in their energy mix.
Recommendations for Improving Customer Retention in the Renewable Energy Sector
Improving customer retention is essential for the long-term success of renewable energy companies. Here are several recommendations:
- Competitive Pricing: Offer competitive pricing structures that are attractive to customers, including fixed-rate options and time-of-use rates that incentivize the use of renewable energy during peak production times.
- Exceptional Customer Service: Provide outstanding customer service that is responsive, helpful, and personalized to meet customer needs. This includes quick response times, easy-to-understand billing, and proactive communication.
- Transparent and Clear Communication: Clearly communicate the benefits of renewable energy, the source of the energy provided, and the environmental impact of the customer’s choice. Avoid jargon and be transparent about pricing and terms of service.
- Innovative Products and Services: Develop innovative products and services, such as smart home integration, energy monitoring tools, and community solar programs, to enhance the customer experience and provide added value.
- Loyalty Programs and Incentives: Implement loyalty programs and incentives to reward customer loyalty and encourage long-term commitment. This could include discounts, rebates, or other benefits.
- Community Engagement: Engage with local communities and support initiatives that promote renewable energy. This could involve partnerships with local organizations, sponsoring educational events, or investing in community solar projects.
- Regulatory Advocacy: Advocate for policies that support renewable energy and create a level playing field for renewable energy suppliers. This includes net metering policies, tax incentives, and other regulatory frameworks that promote renewable energy adoption.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, the story of SunContract’s customer loss is a complex one, highlighting the importance of competitive pricing, superior customer service, and the evolving dynamics of the renewable energy market. This shift underscores the need for energy providers to prioritize customer satisfaction and adapt to the changing needs of consumers. By understanding the reasons behind customer attrition, the industry can better navigate the challenges and foster greater adoption of renewable energy, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Quick FAQs
What is net metering?
Net metering allows customers with solar panels or other renewable energy sources to sell excess energy back to the grid, offsetting their electricity costs.
Why did so many customers leave SunContract?
Customers cited various reasons, including better pricing from competitors, dissatisfaction with customer service, and potentially, limitations in net metering policies compared to those offered by other suppliers.
How does this affect the adoption of renewable energy?
High customer churn can slow down the adoption of renewable energy by creating uncertainty and potentially discouraging new customers from investing in renewable sources.
What can SunContract do to regain customers?
SunContract could improve pricing, enhance customer service, and potentially revise their net metering policies to be more competitive.
What are the benefits of net metering for consumers?
Net metering reduces electricity bills, increases the financial viability of renewable energy investments, and promotes energy independence.