CATL’s recent announcement regarding the certification of its sodium-ion batteries for electric vehicles marks a significant turning point in the EV industry. This breakthrough promises a more sustainable and cost-effective future for electric mobility. This article will delve into the details of CATL’s sodium-ion battery technology, exploring its advantages, technical specifications, and potential impact on the market.
We’ll examine the core principles of sodium-ion batteries, compare them to lithium-ion counterparts, and analyze CATL’s specific innovations. Furthermore, we’ll explore the benefits for both EV manufacturers and consumers, including cost reduction and a more sustainable supply chain. From the environmental advantages to the competitive landscape, we’ll cover everything you need to know about CATL’s sodium-ion batteries and their role in shaping the future of electric vehicles.
CATL’s Sodium-ion Battery Certification Announcement

Source: autoevolution.com
CATL, a leading global manufacturer of lithium-ion batteries and energy storage systems, recently announced a significant milestone: the certification of its sodium-ion batteries for electric vehicles. This achievement marks a crucial step in the commercialization of sodium-ion battery technology and offers a promising alternative to lithium-ion batteries, particularly in the context of the growing electric vehicle market.
Summary of the Announcement
CATL’s announcement focused on the successful certification of its sodium-ion batteries, confirming their readiness for integration into electric vehicles. The company highlighted the completion of various tests and the attainment of certifications demonstrating the batteries’ safety, performance, and compliance with industry standards. This certification signifies that CATL’s sodium-ion batteries meet the necessary requirements for use in EVs, paving the way for mass production and deployment.
Specific Certifications and Standards Met
The certification process involved rigorous testing to ensure the sodium-ion batteries met specific performance and safety standards.CATL’s sodium-ion batteries have been certified to meet or exceed several key standards:
- Safety Standards: The batteries underwent extensive safety testing, including short-circuit, overcharge, and thermal runaway tests. These tests are crucial to ensure the batteries can withstand various operating conditions and potential hazards.
- Performance Standards: The batteries’ performance was evaluated based on criteria such as energy density, power density, and cycle life. These tests assess the battery’s ability to store and deliver energy efficiently over its lifespan.
- Environmental Standards: CATL’s sodium-ion batteries were also evaluated for their environmental impact, including the use of sustainable materials and the recyclability of the battery components. This aligns with the growing emphasis on environmentally friendly technologies in the EV industry.
The specific certifications achieved likely include those from recognized testing organizations, such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories) and other regional or international bodies. The exact certifications obtained and the specific standards met were likely detailed in CATL’s official announcement or supporting documentation.
Significance of the Certification Milestone
The certification of CATL’s sodium-ion batteries holds significant implications for both the company and the electric vehicle industry.
- For CATL: The certification validates CATL’s technological advancements in sodium-ion battery technology, enhancing its competitive position in the battery market. It opens the door for commercialization and mass production of these batteries, allowing CATL to diversify its product offerings and potentially capture a larger market share.
- For the Electric Vehicle Industry: The certification of sodium-ion batteries represents a diversification of battery technology for EVs. Sodium-ion batteries offer several advantages over lithium-ion batteries, including lower material costs and potentially greater resource availability.
- Impact on Battery Costs: The use of sodium-ion batteries could potentially lower the overall cost of electric vehicles. Sodium is more abundant and less expensive than lithium, which could lead to a reduction in battery pack costs.
- Impact on Supply Chain: The certification encourages the development of a more diverse battery supply chain. This is crucial for reducing the reliance on a single type of battery technology and mitigating supply chain risks.
The certification also sets a precedent for other manufacturers in the sodium-ion battery space, potentially accelerating the adoption of this technology and fostering further innovation.
Sodium-Ion Battery Technology
Sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) are emerging as a promising alternative to lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), especially for large-scale energy storage and applications where cost-effectiveness is crucial. They offer a potentially more sustainable and readily available resource base.
Fundamental Principles and Key Components
SIBs operate on principles similar to LIBs, but they utilize sodium ions (Na+) instead of lithium ions (Li+) as the charge carriers. The basic components include a cathode, an anode, an electrolyte, and a separator.* Cathode: This electrode typically contains a sodium-containing compound, such as a layered oxide (e.g., NaMO2, where M is a transition metal like Mn, Fe, or Ni), a polyanionic compound (e.g., Na3V2(PO4)3), or a Prussian blue analogue.
During discharge, sodium ions move from the anode to the cathode.* Anode: The anode can be made of various materials, including hard carbon, soft carbon, or other sodium-based compounds. During discharge, sodium ions are released from the anode.* Electrolyte: The electrolyte is a solution that allows the movement of sodium ions between the cathode and anode.
Common electrolytes include sodium salts dissolved in organic solvents.* Separator: This component is a porous membrane that physically separates the cathode and anode, preventing short circuits while allowing sodium ions to pass through.The overall chemical reaction during discharge can be represented generally as:
Cathode + Anode ↔ Cathode + Anode + Na+ + e-
Where the left side represents the fully charged state, and the right side represents the discharged state. The specific chemical reactions depend on the cathode and anode materials used.
Comparison of Sodium-Ion and Lithium-Ion Batteries
Comparing SIBs and LIBs reveals several key differences, each with advantages and disadvantages. These differences affect their suitability for various applications.* Cost:
Lithium-Ion
Lithium is relatively expensive and geographically concentrated, making LIBs susceptible to price fluctuations and supply chain vulnerabilities.
Sodium-Ion
Sodium is abundant and widely distributed, significantly reducing the raw material cost and enhancing supply chain stability.* Energy Density:
Lithium-Ion
LIBs generally offer higher energy density, meaning they can store more energy per unit of weight or volume. This makes them ideal for applications where space and weight are critical, such as electric vehicles (EVs).
Sodium-Ion
SIBs typically have lower energy density compared to LIBs, although advancements in materials science are steadily improving this aspect. This can be a disadvantage in applications where space and weight are critical.* Resource Availability:
Lithium-Ion
Lithium resources are concentrated in specific regions, which can create geopolitical dependencies and supply chain challenges.
Sodium-Ion
Sodium is one of the most abundant elements on Earth, making it readily available globally. This broad availability reduces resource constraints and supports sustainability.* Operating Voltage:
Lithium-Ion
LIBs usually have higher operating voltages, contributing to their higher energy density.
Sodium-Ion
SIBs typically operate at lower voltages, which can affect the overall energy output and efficiency.* Safety:
Lithium-Ion
LIBs can be prone to thermal runaway, leading to safety concerns under certain conditions.
Sodium-Ion
SIBs are generally considered to be safer due to their inherent chemical properties and lower operating voltages.* Environmental Impact:
Lithium-Ion
The extraction of lithium can have environmental consequences, and the disposal of LIBs requires careful management to avoid environmental pollution.
Sodium-Ion
SIBs potentially offer a lower environmental footprint due to the abundance of sodium and the possibility of using more sustainable materials.
Chemical Reactions During Charge and Discharge Cycles
The chemical reactions in a sodium-ion battery during charge and discharge involve the movement of sodium ions between the cathode and anode. The specific reactions depend on the electrode materials.During discharge:* Sodium ions (Na+) are released from the anode material (e.g., hard carbon).
- These Na+ ions move through the electrolyte and separator to the cathode.
- At the cathode (e.g., a layered oxide), the Na+ ions are inserted into the cathode material, along with electrons from the external circuit.
The overall reaction at the cathode could be represented as
NaMO2 + xNa+ + xe- -> Na2MO2. Where M is the transition metal, x is the number of sodium ions involved.
During charge:* The reverse process occurs.
- Na+ ions are extracted from the cathode material.
- These Na+ ions move through the electrolyte and separator to the anode.
- At the anode, the Na+ ions are inserted into the anode material, along with electrons from the external circuit.
The overall reaction at the anode could be represented as
C + xNa+ + xe- -> NaC. Where C is the carbon material, x is the number of sodium ions involved.
These reactions are facilitated by the electrolyte, which allows the sodium ions to move between the electrodes. The separator prevents direct contact between the electrodes, preventing short circuits and ensuring safe operation. The continuous cycling of these reactions enables the battery to store and release electrical energy.
CATL’s Sodium-Ion Battery
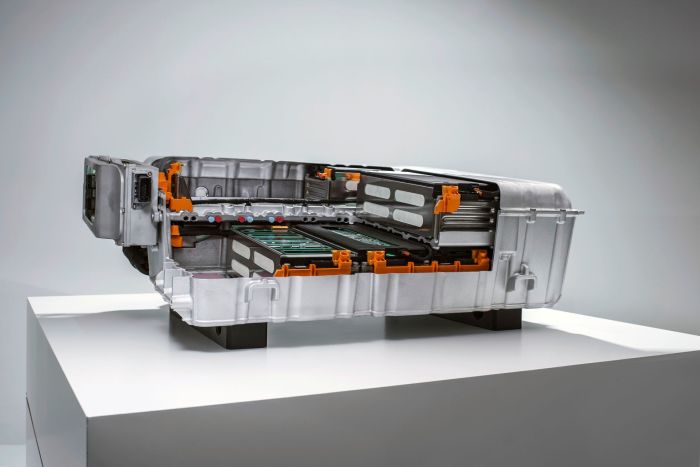
Source: autotech.news
CATL’s certification of sodium-ion batteries marks a significant advancement in battery technology, offering an alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are designed to address concerns about the availability and cost of lithium while maintaining performance characteristics suitable for electric vehicles (EVs). This section focuses on the technical specifications of CATL’s sodium-ion batteries, including their energy density, power output, lifespan, materials, and key performance indicators.
Technical Specifications of CATL’s Sodium-Ion Batteries
CATL’s sodium-ion batteries are engineered to provide a competitive performance profile. These batteries offer a viable alternative to lithium-ion, particularly in applications where cost-effectiveness and resource availability are critical.* Energy Density: CATL’s sodium-ion batteries achieve an energy density that is approaching the performance of lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries. While specific figures can vary depending on the battery cell design and pack configuration, the company has indicated that its sodium-ion batteries have a similar energy density to LFP batteries.
This means they can store a comparable amount of energy per unit of weight or volume, making them suitable for various EV applications.* Power Output: Sodium-ion batteries can deliver a good power output, enabling rapid acceleration and efficient operation of EVs. The power output capabilities are critical for the overall driving experience and performance. CATL’s sodium-ion batteries are designed to provide sufficient power for various EV segments, including city cars and other vehicles where high power demands are not always the primary focus.* Lifespan: The lifespan of a battery is a critical factor determining its long-term value and sustainability.
CATL’s sodium-ion batteries are designed to offer a competitive lifespan, comparable to other battery chemistries. This longevity is crucial for ensuring that the batteries can withstand the demands of regular use in EVs, minimizing the need for replacements and reducing the environmental impact. The exact cycle life (number of charge/discharge cycles before performance degradation) is a critical parameter, and CATL has been working to optimize it.
Materials Used and Sustainability
The materials used in CATL’s sodium-ion batteries are crucial for both performance and sustainability. Sodium-ion batteries utilize sodium, which is abundant and widely distributed globally, offering a significant advantage in terms of resource availability.* Materials: CATL’s sodium-ion batteries typically use materials such as sodium-based cathode materials, which may include compounds like sodium iron phosphate (NaFePO4) or layered oxide materials.
The anode often uses hard carbon or other carbon-based materials. The electrolyte consists of a sodium salt dissolved in an organic solvent.* Sourcing and Sustainability: The sourcing of materials for sodium-ion batteries is designed to be more sustainable than that of lithium-ion batteries. Sodium is abundant, reducing supply chain risks. CATL focuses on responsible sourcing of materials, minimizing environmental impact, and promoting circular economy practices.
This includes reducing waste and optimizing material use. The environmental footprint of sodium-ion batteries is expected to be lower than that of lithium-ion batteries, particularly concerning mining and refining processes.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The following table provides a comparison of key performance indicators for CATL’s sodium-ion batteries compared to industry benchmarks. This comparison helps illustrate the performance capabilities and competitive positioning of the technology. Note that specific values can vary based on battery design and testing conditions.
| KPI | CATL Battery | Industry Benchmark | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Density | 140-160 | 100-200 | Wh/kg |
| Power Output | High (comparable to LFP) | Variable (dependent on chemistry and design) | W/kg |
| Cycle Life | 3,000+ | 2,000-5,000+ | Cycles |
| Operating Temperature Range | -20 to 60 | -20 to 60 | °C |
Benefits of Sodium-Ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles
Sodium-ion batteries offer several advantages for electric vehicles (EVs), potentially transforming both the economics and environmental impact of the automotive industry. These benefits extend to both manufacturers and consumers, promising to make EVs more accessible and sustainable.
Cost Reduction in Electric Vehicles
Sodium-ion batteries have the potential to significantly lower the cost of EVs compared to their lithium-ion counterparts. This cost reduction is primarily due to the abundance and lower cost of sodium compared to lithium.The main cost-saving factors include:
- Material Availability: Sodium is significantly more abundant than lithium, reducing supply chain constraints and price volatility. For example, sodium is the sixth most abundant element on Earth, whereas lithium is much rarer.
- Raw Material Costs: The raw materials used in sodium-ion battery production, such as sodium carbonate, are generally cheaper than those required for lithium-ion batteries. This translates to lower overall battery production costs.
- Simplified Manufacturing: Sodium-ion batteries can potentially use simpler manufacturing processes, further reducing costs. This includes potentially using different materials and designs that are less reliant on expensive components.
This cost reduction translates to a lower overall vehicle price for consumers. Lower battery costs can also lead to more affordable EV models and make EVs competitive with internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
Improving Sustainability of the Electric Vehicle Supply Chain
Sodium-ion batteries can contribute to a more sustainable EV supply chain by reducing reliance on scarce resources and minimizing environmental impact.The sustainability advantages include:
- Reduced Reliance on Lithium and Cobalt: Sodium-ion batteries eliminate or significantly reduce the need for lithium and cobalt, critical minerals often associated with environmental and social concerns related to their extraction.
- Geographical Diversification: The wider availability of sodium can diversify the geographical sources of battery materials, reducing reliance on a few countries and mitigating supply chain risks. This geographical diversification can also promote regional economic development.
- Environmental Impact: The production of sodium-ion batteries may have a lower environmental footprint compared to lithium-ion batteries due to the use of more readily available and potentially less energy-intensive materials. This includes factors such as reduced water usage in extraction processes.
For example, using more abundant and sustainable materials can contribute to a smaller carbon footprint throughout the battery’s lifecycle. This contributes to a more circular economy and aligns with the goals of reducing emissions.
CATL’s Role in the Sodium-Ion Battery Market
CATL’s entry into the sodium-ion battery market signifies a significant shift in the landscape of energy storage for electric vehicles. Their advancements and strategic positioning have the potential to reshape the industry, offering a viable alternative to lithium-ion batteries. This section delves into CATL’s key contributions, competitive advantages, partnerships, and milestones in this emerging technology.
CATL’s Position and Competitive Advantages
CATL has strategically positioned itself as a frontrunner in the sodium-ion battery market, leveraging its existing expertise and resources. Their competitive advantages are multifaceted and contribute to their strong market standing.
- Established Manufacturing Capabilities: CATL benefits from its massive production capacity and global supply chain, allowing for rapid scaling of sodium-ion battery production. This advantage helps them meet the growing demand for electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
- Technological Innovation: CATL’s investment in research and development has led to breakthroughs in sodium-ion battery technology, including improvements in energy density, cycle life, and safety. Their continuous innovation allows them to offer competitive products.
- Cost Efficiency: Sodium-ion batteries, using more abundant materials than lithium, have the potential to be more cost-effective. CATL’s focus on cost optimization and efficient manufacturing processes enhances their competitive edge.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with automotive manufacturers and other industry players provide CATL with access to markets, distribution channels, and valuable feedback for product development. These partnerships support market penetration and adaptation.
- Scalability and Adaptability: CATL’s manufacturing facilities are designed to handle both lithium-ion and sodium-ion battery production, providing flexibility to meet market demands and adjust to changing material availability.
Partnerships and Collaborations
CATL has established several strategic partnerships and collaborations to accelerate the development and deployment of sodium-ion battery technology. These collaborations span across the automotive, energy storage, and materials supply sectors.
- Automotive Manufacturers: CATL partners with leading electric vehicle manufacturers to integrate sodium-ion batteries into their vehicles. This provides CATL with valuable insights into the specific needs of the automotive market and enables them to tailor their battery solutions.
- Material Suppliers: Collaborations with material suppliers secure a stable supply of key components for sodium-ion batteries, such as sodium-based cathode materials and electrolytes. These partnerships are crucial for ensuring the long-term viability of sodium-ion battery production.
- Energy Storage System Providers: CATL collaborates with energy storage system providers to deploy sodium-ion batteries in stationary energy storage applications. This allows them to diversify their market reach and capitalize on the growing demand for grid-scale energy storage.
- Research Institutions: CATL partners with research institutions and universities to conduct joint research and development projects. These collaborations provide access to cutting-edge technologies and expertise, fostering innovation in battery materials and manufacturing processes.
Timeline of Milestones
CATL’s journey in developing and commercializing sodium-ion batteries has been marked by significant milestones, demonstrating their commitment and progress in this field.
- Early Research and Development (Pre-2021): CATL initiates research and development efforts in sodium-ion battery technology, focusing on material selection, cell design, and manufacturing processes. They invest in R&D to lay the foundation for future advancements.
- Prototype Development and Testing (2021): CATL unveils its first generation of sodium-ion batteries, demonstrating competitive performance characteristics. Rigorous testing and validation are conducted to ensure safety and reliability.
- Pilot Production and Partnerships (2022): CATL initiates pilot production of sodium-ion batteries and establishes strategic partnerships with automotive manufacturers and other industry players. This phase focuses on scaling up production and securing market opportunities.
- Commercialization and Market Entry (2023-Present): CATL begins commercial production and mass deployment of sodium-ion batteries in electric vehicles and energy storage systems. They aim for rapid market penetration and expansion.
- Ongoing Innovation and Expansion (Future): CATL continues to invest in research and development, aiming to improve the performance, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability of sodium-ion batteries. They are also expanding their production capacity and market reach.
Challenges and Future Prospects of Sodium-Ion Batteries

Source: bigcommerce.com
While CATL’s Sodium-ion battery certification is a significant step, the widespread adoption of sodium-ion batteries faces hurdles. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for realizing their full potential in the electric vehicle market and beyond. This section will explore the current obstacles and the ongoing efforts to enhance sodium-ion battery technology.
Current Challenges Facing Sodium-Ion Battery Adoption
Several key challenges currently limit the widespread adoption of sodium-ion batteries in electric vehicles. Addressing these issues is paramount for the technology’s future success.
- Energy Density: Sodium-ion batteries, in their current state, generally exhibit lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries. This means they store less energy for the same weight or volume. This translates to shorter driving ranges for electric vehicles using sodium-ion batteries. For instance, a typical lithium-ion battery pack might offer a range of 300 miles, while a comparable sodium-ion battery pack might only achieve 200 miles.
This difference is a significant barrier to consumer acceptance.
- Power Density: The power density of sodium-ion batteries is also often lower. This affects the battery’s ability to deliver high power output, impacting acceleration and overall vehicle performance. A lower power density can result in slower acceleration compared to vehicles equipped with lithium-ion batteries.
- Cycle Life: The cycle life, or the number of charge-discharge cycles a battery can withstand before its performance degrades, can be a challenge. Sodium-ion batteries, in some cases, have a shorter cycle life than their lithium-ion counterparts. This can lead to the need for more frequent battery replacements, increasing the total cost of ownership for electric vehicle owners.
- Cost: Although sodium is abundant and the raw materials used in sodium-ion batteries can be cheaper than those in lithium-ion batteries, the overall manufacturing process and economies of scale are still developing. The cost-effectiveness of sodium-ion batteries needs to be competitive with established lithium-ion battery technologies to drive widespread adoption.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Sodium-ion batteries can be more sensitive to temperature fluctuations than lithium-ion batteries, potentially affecting their performance in extreme hot or cold weather conditions. This requires sophisticated battery management systems (BMS) to regulate temperature and ensure optimal operation.
Research and Development Efforts for Performance Improvement
Significant research and development efforts are underway to address the challenges Artikeld above and improve the performance of sodium-ion batteries. Scientists and engineers are actively working on various aspects to enhance their capabilities.
- Electrode Materials: Research focuses on developing new electrode materials with higher energy and power densities. This includes exploring different cathode materials, such as Prussian blue analogues, layered oxides, and hard carbons, to improve energy storage capacity. The use of new anode materials, such as hard carbon, is also being explored.
- Electrolyte Development: The electrolyte plays a crucial role in battery performance. Researchers are working on developing improved electrolytes that enhance ion conductivity, reduce internal resistance, and improve the battery’s operating temperature range. This includes exploring new salt and solvent combinations to optimize performance.
- Battery Architecture and Design: Optimizing battery architecture and design can significantly impact performance. This includes exploring different cell designs, such as pouch cells and cylindrical cells, and optimizing the battery pack configuration for better energy density and thermal management.
- Battery Management Systems (BMS): Advanced BMS are essential for managing and controlling sodium-ion batteries. Researchers are developing sophisticated BMS to monitor battery health, regulate temperature, and optimize charging and discharging processes to extend battery life and enhance performance.
- Material Science Innovations: Innovations in material science are crucial for improving the overall performance of sodium-ion batteries. This includes developing new materials with enhanced properties, such as high ionic conductivity, improved stability, and reduced degradation rates.
Potential Future Applications Beyond Electric Vehicles
The versatility of sodium-ion batteries extends beyond electric vehicles, offering potential applications in various sectors. These alternative uses are driven by the abundance of sodium and the potential for lower costs.
- Grid-Scale Energy Storage: Sodium-ion batteries are well-suited for grid-scale energy storage, where cost-effectiveness and long cycle life are critical. They can store excess energy generated from renewable sources like solar and wind power, helping to stabilize the grid and ensure a reliable power supply. A large-scale energy storage facility, using sodium-ion batteries, could help to manage peak demand and improve grid stability.
- Portable Power Tools and Devices: The lower cost and safety of sodium-ion batteries make them attractive for portable power tools and small electronic devices. Their use can reduce the reliance on lithium-ion batteries in these applications.
- Electric Bikes and Scooters: Sodium-ion batteries can be a viable option for electric bikes and scooters, offering a cost-effective alternative to lithium-ion batteries. This can make electric mobility more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
- Off-Grid Energy Systems: Sodium-ion batteries can be used in off-grid energy systems, such as those used in remote locations or developing countries. They can provide a reliable and affordable source of power for homes, businesses, and other applications.
- Aerospace Applications: Due to their safety and potentially lower cost, sodium-ion batteries are being explored for aerospace applications, where weight and safety are critical considerations. Their use can improve the efficiency and safety of aircraft and spacecraft.
Market Impact and Competitive Landscape
CATL’s certification of sodium-ion batteries marks a significant development in the electric vehicle (EV) market. This technology has the potential to reshape the competitive landscape, influencing both battery manufacturers and EV producers. The impact will be felt across several dimensions, including cost, performance, and the availability of raw materials.
Potential Impact on the Electric Vehicle Market
The introduction of sodium-ion batteries, particularly from a major player like CATL, could have a profound effect on the EV market. Sodium-ion batteries offer several advantages that could make EVs more accessible and affordable for a wider range of consumers. The primary impact is likely to be on the cost of EVs. Since sodium is abundant and inexpensive compared to lithium, the cost of sodium-ion batteries could be lower, potentially driving down the overall price of EVs.Another area where sodium-ion batteries could make a difference is in the performance characteristics of EVs.
While sodium-ion batteries may not offer the same energy density as lithium-ion batteries, they could still provide sufficient range for many applications, especially in urban settings and for smaller vehicles. Furthermore, sodium-ion batteries can operate effectively in low-temperature environments, which could improve the performance of EVs in colder climates. This could lead to an increase in the adoption rate of EVs in regions with colder weather conditions.
Comparison with Competitors’ Sodium-Ion Battery Technology
The competitive landscape for sodium-ion batteries is still developing, but several companies are working on this technology. CATL’s certification and mass production plans put it in a leading position, but other players are also making progress. A comparison of the technology of CATL and its competitors is useful to understand the relative strengths and weaknesses of each player.* HiNa Battery: HiNa Battery, a Chinese company, is another key player in the sodium-ion battery market.
They have developed sodium-ion batteries with high energy density and cycle life.
Faradion (acquired by Reliance New Energy Solar)
Faradion, a UK-based company that was acquired by Reliance New Energy Solar, focused on developing sodium-ion battery technology for various applications. They claimed to have a high energy density and long cycle life.
Other Companies
Other companies, including companies in China and South Korea, are also actively developing and testing sodium-ion battery technology.
Electric Vehicle Manufacturers Interested in Adopting CATL’s Sodium-Ion Battery Technology
Several EV manufacturers could be potential customers for CATL’s sodium-ion batteries. The interest would be driven by the potential cost savings and the ability to offer EVs at more competitive prices.The following is a list of major EV manufacturers that might be interested in adopting CATL’s sodium-ion battery technology:
- BYD: As a major Chinese EV manufacturer and a significant battery producer, BYD could integrate CATL’s sodium-ion batteries into its product line. BYD has a strong presence in the Chinese market and is expanding globally.
- SAIC Motor: Another major Chinese automaker, SAIC Motor, could benefit from CATL’s sodium-ion batteries, particularly for its mass-market EV models. SAIC has a diverse portfolio of brands and a large production capacity.
- Geely: Geely, another prominent Chinese automaker, could be a potential customer for CATL’s sodium-ion batteries. Geely has been rapidly expanding its EV offerings and has a global presence.
- Renault: Renault, a major European automaker, could use CATL’s sodium-ion batteries to produce more affordable electric vehicles. Renault has a strong position in the European market and is expanding its EV offerings.
- Volkswagen: Volkswagen, a global automotive giant, could use CATL’s sodium-ion batteries for its entry-level EVs. This could make VW more competitive in the mass market.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Sodium-ion batteries, as developed by CATL, offer significant environmental advantages compared to their lithium-ion counterparts. This is crucial for promoting a more sustainable energy future, particularly in the context of electric vehicles. The shift towards sodium-ion technology can help mitigate some of the environmental challenges associated with lithium-ion battery production and disposal.
Environmental Advantages of Sodium-Ion Batteries
Sodium-ion batteries present several environmental benefits, primarily stemming from the abundance and distribution of sodium compared to lithium. The sourcing and processing of sodium can also be less environmentally intensive.
- Resource Abundance and Availability: Sodium is significantly more abundant than lithium. This greater availability reduces the risk of supply chain disruptions and minimizes the environmental impact associated with resource extraction. Sodium can be extracted from readily available sources like seawater and common salt, unlike lithium, which often requires mining in environmentally sensitive areas. For example, according to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the estimated global reserves of sodium are vastly greater than those of lithium, offering a more sustainable and secure supply chain.
- Reduced Mining Impact: The extraction of lithium can involve significant environmental damage, including water depletion and habitat destruction, especially in regions with arid climates. Sodium extraction, with sources like seawater and salt deposits, generally has a lower environmental footprint. This is a crucial advantage as the demand for electric vehicles increases and the need for sustainable battery materials grows.
- Potential for Local Sourcing: The widespread availability of sodium allows for the potential of localized sourcing, reducing transportation emissions and the overall carbon footprint of battery production. This can lead to a more circular economy where materials are sourced and processed closer to manufacturing facilities, lowering the environmental impact.
- Improved Recycling Prospects: While the recycling infrastructure for sodium-ion batteries is still developing, the simpler chemistry and more common materials used in their construction could potentially lead to easier and more efficient recycling processes. This could reduce waste and the need for new raw materials, contributing to a more circular economy.
Sodium-Ion Batteries in a Sustainable Energy Future
Sodium-ion batteries play a pivotal role in fostering a sustainable energy future, particularly in conjunction with renewable energy sources. Their characteristics make them well-suited for grid-scale energy storage and other applications.
- Grid-Scale Energy Storage: Sodium-ion batteries are well-suited for grid-scale energy storage, which is essential for integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. These batteries can store excess energy generated during peak production times and release it when demand is high, helping to stabilize the grid and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. This contributes to a more reliable and sustainable energy supply.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: By utilizing more abundant materials and potentially requiring less energy-intensive manufacturing processes, sodium-ion batteries can contribute to a lower overall carbon footprint compared to lithium-ion batteries. This aligns with global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
- Decentralized Energy Systems: Sodium-ion batteries can facilitate the development of decentralized energy systems, such as microgrids and off-grid power solutions. This can improve energy access in remote areas and reduce the environmental impact associated with long-distance energy transmission.
- Complementing Lithium-Ion Batteries: Sodium-ion batteries are not necessarily a replacement for lithium-ion batteries in all applications. They can complement lithium-ion technology, particularly in areas where cost and sustainability are critical factors, such as in stationary energy storage and certain types of electric vehicles. This diversified approach ensures that the most appropriate battery technology is used for each specific application, maximizing environmental benefits.
Key environmental benefits of sodium-ion batteries include:
- Abundant and readily available resources.
- Reduced mining impact.
- Potential for local sourcing.
- Improved recycling prospects.
- Contribution to a lower carbon footprint.
Visual Representation
Visual representations are crucial for understanding the complex technology behind CATL’s sodium-ion batteries. These illustrations and diagrams offer insights into the battery’s internal workings, its integration within an electric vehicle (EV), and the dynamic processes of charging and discharging. This section provides detailed descriptions of such visual representations.
Internal Structure of a CATL Sodium-Ion Battery
The internal structure of a CATL sodium-ion battery can be visualized through a detailed cross-sectional diagram. This diagram reveals the arrangement and composition of the battery’s core components.
- Anode: The anode, typically made of hard carbon, is shown as a layered structure. The hard carbon material is chosen for its ability to effectively intercalate sodium ions.
- Cathode: The cathode, a crucial component, is depicted as a layered structure, often composed of materials such as Prussian white analogs or other sodium-based compounds. This material’s design is optimized for efficient sodium ion storage and release.
- Electrolyte: The electrolyte, a liquid or solid substance, fills the space between the anode and cathode. The diagram illustrates the electrolyte’s role in facilitating the movement of sodium ions. The electrolyte is typically a solution of a sodium salt in an organic solvent.
- Separator: A thin, porous separator, positioned between the anode and cathode, is clearly visible. This separator prevents direct contact between the electrodes while allowing sodium ions to pass through, ensuring the battery’s safe operation.
- Current Collectors: Copper and aluminum foils serve as current collectors, efficiently gathering and distributing electrons during charging and discharging. These are shown in direct contact with the anode and cathode materials, respectively.
- Overall Arrangement: The diagram highlights the layered arrangement of these components, with the anode, separator, cathode, and electrolyte carefully arranged within the battery cell. The entire assembly is encased within a protective casing.
Battery Pack Design and Integration in an Electric Vehicle
An image showcasing the battery pack of an electric vehicle using CATL’s sodium-ion batteries demonstrates the design and integration of these batteries within the vehicle’s structure.
- Modular Design: The battery pack is depicted as a modular system, consisting of multiple battery modules. Each module contains a series of individual sodium-ion battery cells. This modular approach allows for flexibility in designing battery packs to fit various vehicle sizes and configurations.
- Arrangement within the Vehicle: The battery pack is shown integrated within the vehicle’s chassis, typically beneath the floor of the vehicle. This placement optimizes space utilization and lowers the vehicle’s center of gravity, enhancing stability.
- Thermal Management System: A thermal management system, including cooling channels and heat sinks, is visually represented. This system is crucial for regulating the battery’s temperature, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
- Electrical Connections and Wiring: The diagram illustrates the electrical connections and wiring that link the battery modules to the vehicle’s power electronics, including the inverter and motor.
- Protective Casing: A robust protective casing surrounds the battery pack, providing protection against physical damage and environmental factors such as water and dust.
- Overall Aesthetics: The image reflects a streamlined and compact design, optimized for efficient energy storage and integration within the vehicle’s overall architecture.
Charging and Discharging Process Visualized
A visual representation of the battery’s charging and discharging process uses animated diagrams to illustrate the movement of sodium ions and electrons.
- Discharging Process: During discharging, the diagram shows sodium ions moving from the anode to the cathode through the electrolyte, as electrons flow from the anode to the cathode through an external circuit. This flow of electrons provides the electrical power that drives the electric vehicle.
- Charging Process: During charging, the diagram shows the reverse process. Sodium ions move from the cathode back to the anode through the electrolyte, while electrons move from an external power source to the anode.
- Electrolyte Dynamics: The animation illustrates the role of the electrolyte in facilitating the sodium ion transport.
- Electron Flow in the External Circuit: The animation clearly depicts the flow of electrons through the external circuit, illustrating how electrical energy is supplied or consumed.
- Energy Levels and Voltage: The diagram may incorporate graphs or charts showing the voltage and energy levels of the battery during charging and discharging, demonstrating the relationship between these parameters and the battery’s state of charge.
- Material Changes: Subtle visual cues, such as color changes or the expansion/contraction of electrode materials, could be used to illustrate the changes occurring within the battery during charging and discharging.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, CATL’s certified sodium-ion batteries represent a major step forward in the EV revolution. These batteries offer a compelling alternative to traditional lithium-ion technology, with the potential to lower costs, enhance sustainability, and drive wider adoption of electric vehicles. As CATL continues to innovate and expand its market presence, the future of EVs looks brighter than ever, paving the way for a greener and more accessible transportation landscape.
Key Questions Answered
What are the main advantages of sodium-ion batteries compared to lithium-ion batteries?
Sodium-ion batteries offer several advantages, including lower material costs (sodium is more abundant), potentially better safety, and the ability to operate effectively in a wider range of temperatures.
How does the energy density of CATL’s sodium-ion batteries compare to lithium-ion batteries?
While sodium-ion batteries generally have a lower energy density than lithium-ion batteries, CATL is working to close this gap. Their latest models are approaching competitive energy densities, making them suitable for various EV applications.
Are sodium-ion batteries as durable as lithium-ion batteries?
CATL’s sodium-ion batteries are designed for a long lifespan, comparable to many lithium-ion batteries. The exact lifespan depends on the specific battery design and usage conditions, but they are expected to provide reliable performance over many charge-discharge cycles.
What types of electric vehicles are best suited for sodium-ion batteries?
Sodium-ion batteries are particularly well-suited for smaller electric vehicles, such as city cars, and potentially for energy storage systems. They can also be used in larger vehicles, depending on the energy density and performance requirements.
How does the environmental impact of sodium-ion batteries compare to lithium-ion batteries?
Sodium-ion batteries generally have a lower environmental impact due to the abundance of sodium and the potential for using more sustainable materials in their construction. This can lead to a reduced carbon footprint throughout the battery’s lifecycle.
